Spot VMs Overview: The Affordable Google Discount
What are Spot VMs?
Google has a massive infrastructure distributed throughout the globe and a dynamic mix of workloads, which implies that some of its infrastructure capacity may remain idle. Spot VMs are Compute Engine VMs that utilize this idle capacity whenever it is accessible. Spot VMs are extremely cost-effective compute instances appropriate for batch tasks and fault-tolerant workloads.
Features
● Same machine types as standard VMs
● Offered at 60-91% discount
● No performance differences compared to standard VMs (refer to Performance comparison (on-demand vs Spot) section of this article).
● Useful for stateless, fault tolerant or batch workloads
● Spot VMs have no expiration time. Only terminated when Compute Engine needs resources for standard VMs
Limitations
● Spot VMs are idle capacity, therefore they might not always be available.
● Not covered by any other SLA and are not included in the Compute Engine Service Level Agreement (SLA).
● Cannot be used with Google Cloud Free Tier credits for Spot VMs.
Pricing for Spot VMs
Customers who run workloads at a drastically reduced rate can choose to do so profitably thanks to GCP Spot pricing. These prices change over time, up to once every 30 days. Spot VMs provide at least a 60% discount and up to a 91% discount on the price of standard VMs with the same machine types.
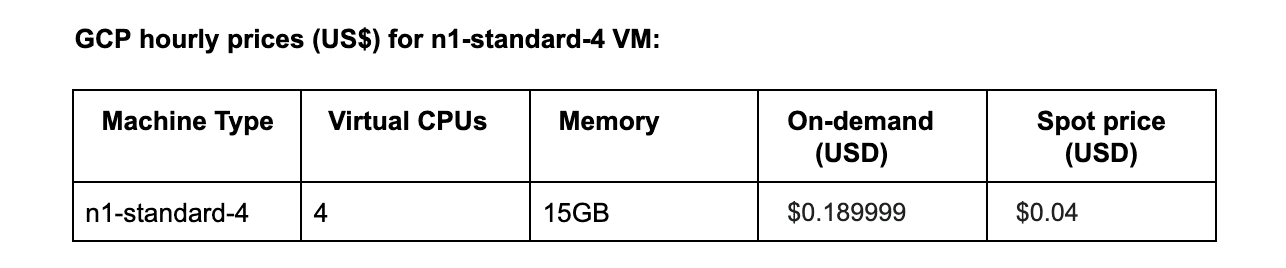
These prices change over time, up to once every 30 days. Spot VMs provide at least a 60% discount and up to a 91% discount on the price of standard VMs with the same machine types.
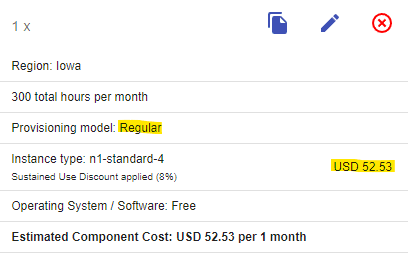
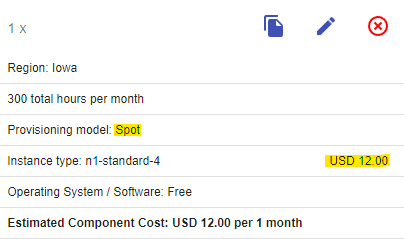
Note: As mentioned above, Spot pricing can change over time up to once every 30 days.
Difference Between Preemptible VM and Spot VM
The Preemptible VM can be terminated on or before 24 hours after it has been created. The Spot VM has no such restriction. However, both VMs can be reclaimed after a 30-second notification. Preemptible and Spot VMs use the same pricing model as mentioned above.
Preemption of Spot VMs
The actions taken by Compute Engine to preempt Spot VMs are as follows:
- The VM receives a preemption notification from Compute Engine in the form of an ACPI G2 Soft Off signal. Before the VM shuts down, you can handle the preemption notice and perform cleanup tasks using a shutdown script.
- After 30 seconds, if the VM is still running, Compute Engine notifies the operating system with an ACPI G3 Mechanical Off signal.
- Depending on the termination action you set for each VM, the final state of Spot VMs varies: ○ The VM is stopped by the Compute Engine and moves into the TERMINATED state if the termination action is set to STOP or not specified.
- The virtual machine is deleted by Compute Engine if the termination action is set to DELETE.
Managed Instance Groups
Spot VMs can be used in a managed instance group specifying the options for creating Spot VMs in an instance template before you create or update the group. Managed instance groups will create or add new spot VMs when additional compute engine resources are available. This means that managed instance groups do not guarantee Spot capacity.
Steps to Create MIG with Spot VMs
1. Specify the option for creating Spot VMs in an instance template.
2. Create instance group.
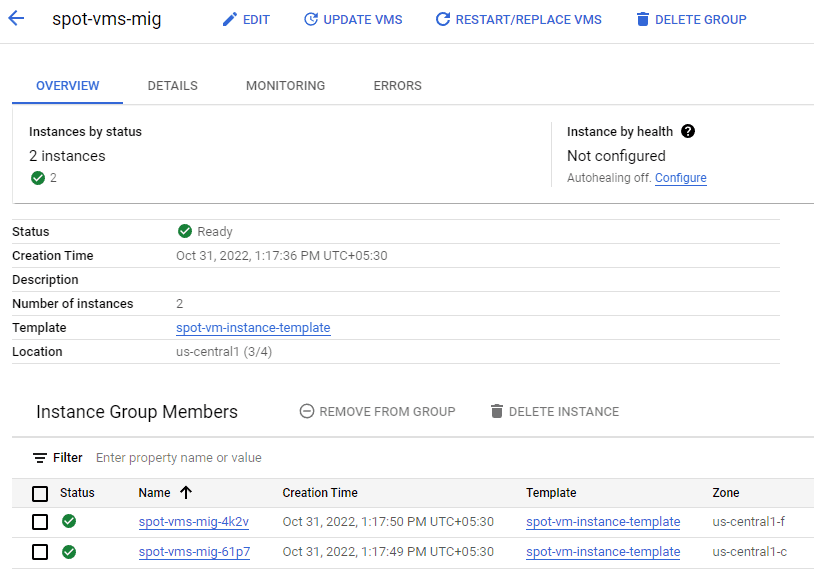
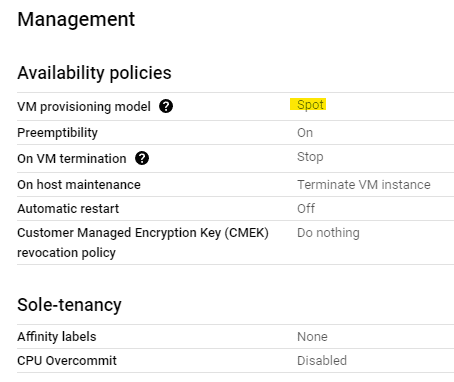
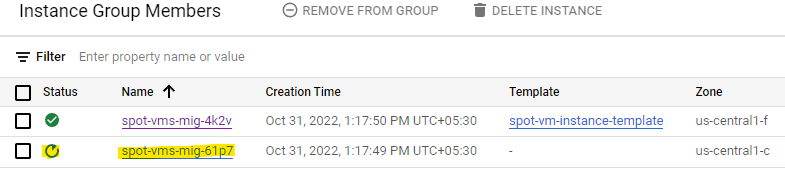
3. If spot instances are preempted, the MIG will continue to attempt to create them.
Google Kubernetes Engine
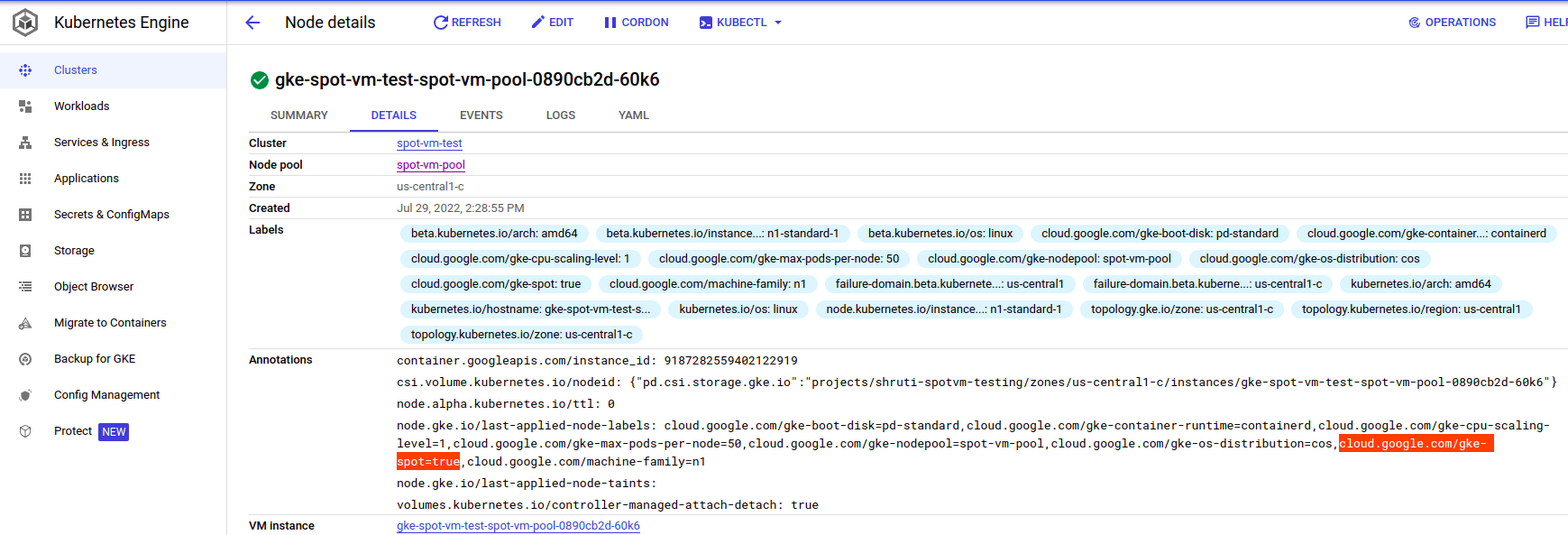
Spot VMs can be used in GKE clusters and node pools to run stateless, batch or fault-tolerant workloads that can tolerate disruptions caused by the ephemeral nature of Spot VMs. When a GKE cluster or node pool with Spot VMs are created, GKE creates underlying compute engine Spot VMs that behave like a managed instance group. Spot VMs using nodes operate similarly to regular GKE nodes, however there is no availability guarantee.
Working with Spot VMs in GKE
1. Use the following commands to create a GKE cluster with 2 node pools: one with Spot VMs and the other with Standard VMs.
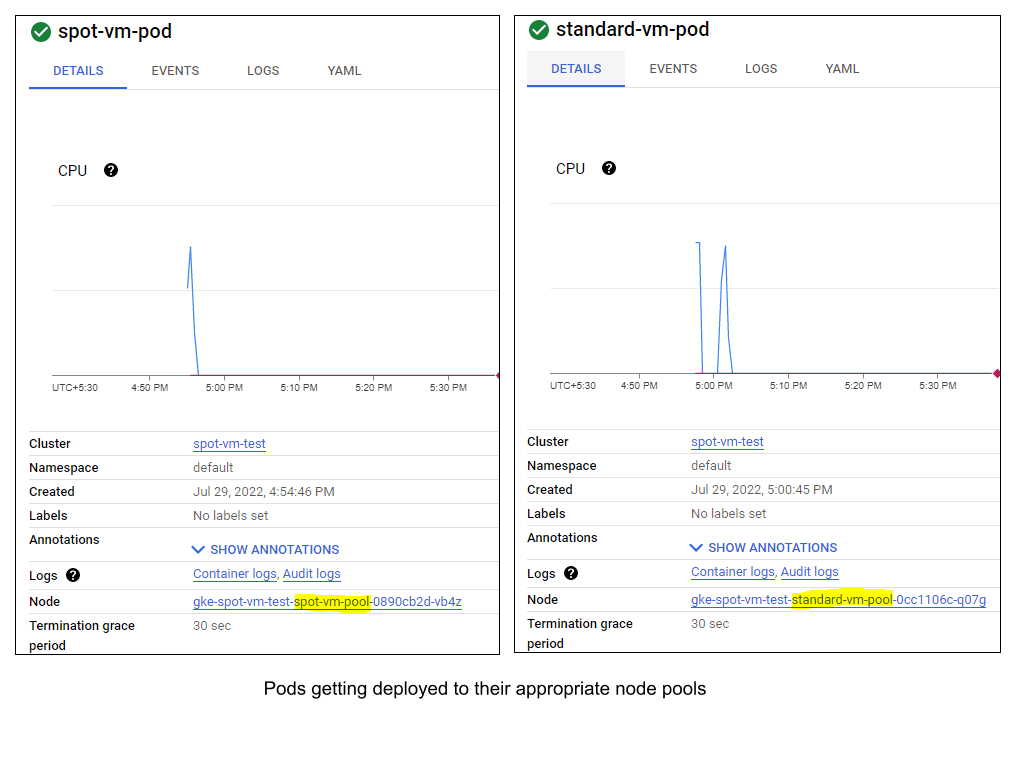
2. GKE automatically adds the “cloud.google.com/gke-spot=true” label to nodes that use Spot VMs. Specific pods can be scheduled on nodes that use Spot VMs using the nodeselector field in pod spec. Add the appropriate nodeSelector field for both the pod definition files.
spot-vm-pod.yaml
spot-vm-pod.yaml
Performance Comparison: On-demand vs. Spot VMs
There is no performance difference between on-demand VMs and Spot VMs. In order to test this, we created two Compute Engine VMs: a Spot VM and a Standard VM, both with the machine type n1-standard2. On both of these VMs, we installed Apache Web Server. Next, we used a tool called Siege, which is an open-source tool for HTTP load testing and benchmarking, to create some load on these VMs. With 25 concurrent requests, we generated load on the VMs for 30 minutes. The performance of the 2 VMs was then compared using a few sample metrics on monitoring dashboards. These are the outcomes:
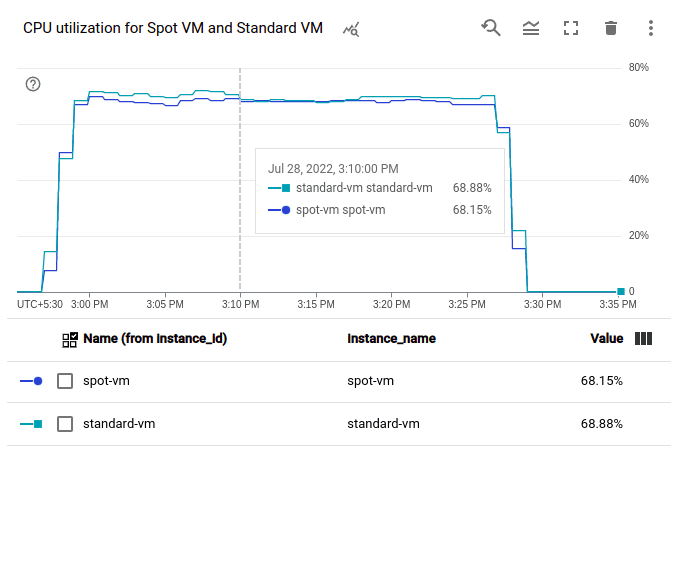
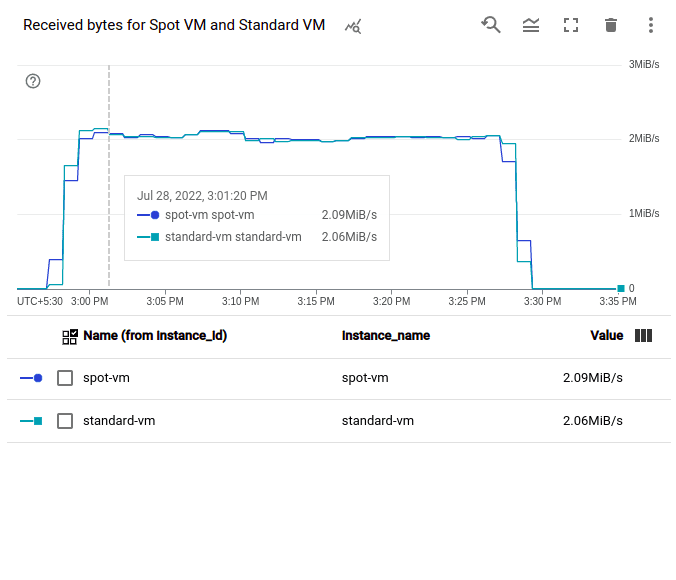
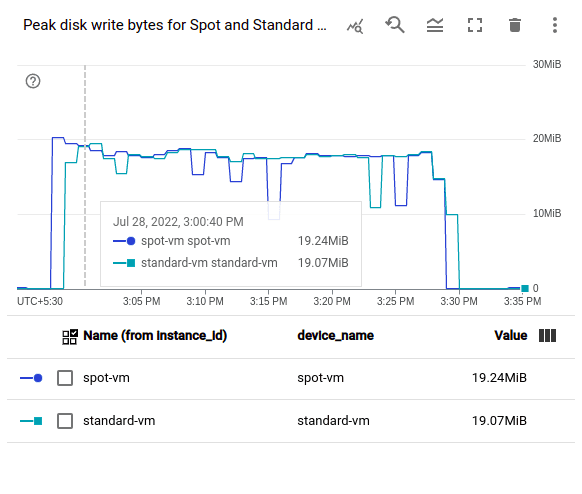
From the above images, it is clear that there are no differences between the Spot VM and Standard VM in terms of CPU, network and disk performance.
Best Practices for Using Spot VMs
As resources for Spot VMs come out of excess and backup Google cloud capacity, smaller machine types are more likely available. Design the applications to be fault and preemption tolerant Manage shutdown and preemption notices (in MIG’s) with a shutdown script that can save a job’s progress so that it can pick up where it left off. For GKE, clusters have a mix of node pools that use Spot VMs and node pools that use standard compute engine VMs ensure that your workloads and jobs are processed even when no Spot VMs are available.
Conclusion
Spot VMs offer an incredible opportunity to slash your cloud compute costs by up to 91%, making them ideal for batch jobs, fault-tolerant workloads, and other non-critical tasks. As highlighted in this blog, Spot VMs provide the same performance as standard VMs while leveraging unused Google Cloud capacity. However, their ephemeral nature requires careful planning and execution.
Our 66degrees experts possess deep expertise in optimizing cloud infrastructure and maximizing Spot VM utilization. Connect with us today for guidance leveraging your Spot VMs and achieve remarkable cost savings without compromising performance or reliability.


